If you think Google is the only one crawling your website, recheck your server logs.
Along with the usual Googlebot crawler, you’ll now see names like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, CCBot, and Google Extended. These aren’t errors, they’re AI crawlers. And they’re changing how your content is found, analyzed, and reused across the internet.
This shift matters because the competition is no longer just about ranking on Google. It’s about how AI systems read your content, interpret your meaning, and decide whether your brand deserves to appear in AI-generated answers.
So let’s break down the real difference in this AI Crawlers vs Google Bot comparison and why your content strategy now needs to support both worlds.
Googlebot Is a Search Crawler. AI Crawlers Are Language Learners.
The Googlebot crawler was built for one job: To discover, index, and rank pages in Google Search.
It follows links, understands site structure, analyzes meta tags, respects robots.txt, and indexes content so Google can rank it. AI crawlers, on the other hand, have a completely different intention. They don’t crawl to rank you, they crawl to learn from you.
Bots like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and Google Extended gather full text content to train large language models (LLMs) or to support answer engines like ChatGPT or Perplexity. Their goal isn’t indexing. It’s understanding your meaning, tone, and authority.
That’s why comparing Google vs AI Web Crawlers isn’t just technical, it’s strategic.
AI Crawlers vs Google Bot: Key Differences
Below is the simplest, clearest comparison you’ll find.
| Factor | Google Bot (Traditional Search) | AI Crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended) |
| Primary Purpose | Index web pages for Google Search | Gather content to train LLMs and answer engines |
| How They Read Pages | Renders pages, executes JavaScript | Mostly raw HTML, often no JavaScript execution |
| Crawl Behavior | Efficient, structured, link-based | Bulk data pulls, full content retrieval |
| What They Prioritize | Relevance, performance, structure | Semantic meaning, clarity, authority |
| Data Pulled Per Request | ~50 KB on average | ~130 KB on average (much heavier) |
| Robots.txt Compliance | Always obeys | Often obeys, but varies by crawler |
| Technical SEO Impact | Direct ranking factor | Indirect influences AI visibility & citations |
| Examples | Googlebot crawler, Google web crawlers | GPTBot, ClaudeBot, CCBot, Google Extended |
Why These Differences Matter
When you understand the gap between Google crawlers vs AI crawlers, you start to see the bigger picture.
Google decides whether you appear in search results.
AI crawlers decide whether you appear in AI-generated answers.
Both matter.
But AI systems rely more heavily on:
- semantic clarity
- clean structure
- brand authority
- fresh information
- machine-friendly formatting
- content available without JavaScript
If AI crawlers can’t read your content clearly, you might rank on Google but still be invisible inside ChatGPT or Perplexity answers.
This is why AI Crawlers vs Google Bot is now one of the most important SEO conversations.
How to Optimize for Both Googlebot and AI Crawlers
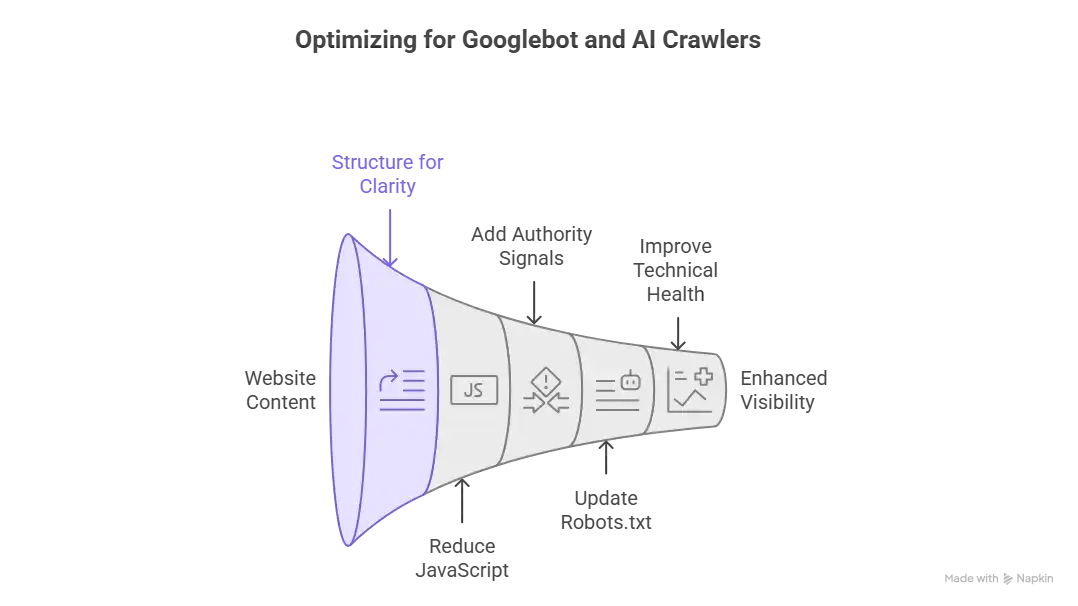
1. Make Your Content Easy for Machines to Understand
AI engines need a clean structure. Use:
- clear H1–H3
- short paragraphs
- direct answers
- semantic cues (“Here’s the key point…”)
This helps both the Googlebot crawler and AI crawlers extract meaning.
2. Reduce JavaScript Dependency
Most AI web crawlers don’t execute JavaScript, which means they can miss important content that loads dynamically. To stay visible, make sure your key information appears in static HTML or is rendered server-side so both Googlebot and AI crawlers can read it without issues.
3. Add Strong Authority Signals
AI models prioritize:
- expert authors
- credible sources
- unique data
- consistent brand mentions
LLMs cite trustworthy sources, not just keyword-optimized pages.
4. Update Your Robots.txt Thoughtfully
You can block or allow AI crawlers specifically:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Disallow: /
Or allow them if you want visibility in AI answers.
5. Improve Technical Health
Good Core Web Vitals and a clear site structure help in two powerful ways: Googlebot can index your pages more efficiently, and AI crawlers can interpret your content more accurately. This is the common ground where Google vs AI web crawlers work together to boost your visibility.
The Future: SEO + AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
Google search gives you rankings.
AI engines give you citations and visibility in answers.
If you want your brand to appear in AI-generated responses, your content needs:
- clarity
- trust
- structure
- machine readability
- semantic depth
This is what LLMs use to choose sources.
Ignoring this new landscape means falling behind, even if your Google SEO is strong.
Final Thoughts
The real question isn’t just “Who is crawling my website?” It’s “Who is interpreting my content, and are they choosing me?” Because today, showing up in Google is only half the game. The other half is making sure AI crawlers can read, understand, and trust your content enough to include it in AI-generated answers.
When you understand the difference between AI Crawlers vs Google Bot, you’re no longer optimizing blindly. You’re preparing your content for both worlds: traditional search rankings and AI-driven discovery. And in a landscape where users rely more on answers than links, that’s a major competitive advantage.






